Stem Cells. 2019;37(8):1018-1029.


hnRNP-K targets open chromatin in mouse embryonic stem cells in concert with multiple regulators
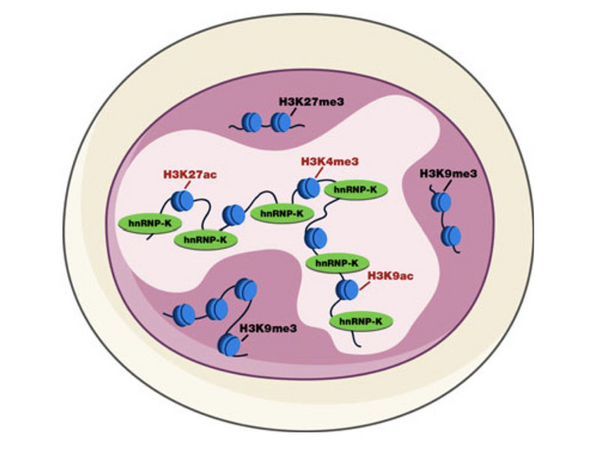
The transcription factor Oct4 plays a key regulatory role in the induction and maintenance of cel-lular pluripotency. With this paper, we show that ubiquitous and multifunctional poly(C)DNA/RNA-binding protein hnRNP-K occupiesOct4(Pou5f1) enhancers in embryonic stem cells(ESCs) but is dispensable for the initiation, maintenance, and downregulation ofOct4geneexpression. Nevertheless, hnRNP-K has an essential cell-autonomous function in ESCs to main-tain their proliferation and viability. To better understand mechanisms of hnRNP-K action in ESCswe have performed ChIP-seq analysis of genome-wide binding of hnRNP-K and identified severalthousands of hnRNP-K target sites that are frequently co-occupied by pluripotency-related and common factors (Oct4, TBP, Sox2, Nanog, Otx2, etc.), as well as active histone marks. Further-more, hnRNP-K localizes exclusively within open chromatin, implying its role in the onset and/ormaintenance of this chromatin state.