Prof. Dr. Roland Schüle (CIBSS-PI), Department of Urology and Centre for Clinical Research (University Medical Center Freiburg, Faculty of Medicine)
Prof. Dr. Manfred Jung (CIBSS-AI), Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences (Faculty of Chemistry and Pharmacy), University of Freiburg
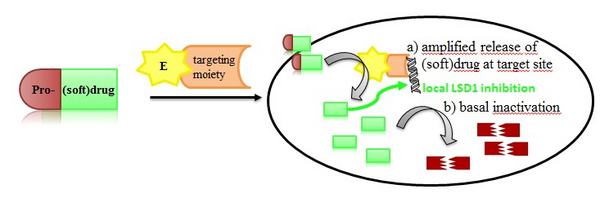
Epigenetics covers inheritable patterns of gene regulation that are encoded by mechanisms other than alterations in the genome. We want to develop a new chemical approach to precisely edit the epigenome in a gene specific manner instead of the established genome-wide action of epigenetic drugs. We propose gene targeting with CRISPR/dCas9 constructs that maintain a gene targeting selectivity but do not cut DNA anymore. They function as a homing device to certain genomic loci and it has already been shown that epigenetic enzymes can be used as cargo and lead to altered epigenetic patterns in defined genomic regions. In our approach, we will fuse an enzyme to the targeting device that will release epigenetically active inhibitors from inactive prodrugs
Thus, e.g. a controlled release of a lysine demethylase inhibitor would induce hypermethylation effectively. We have already prepared such prodrugs that can be released by a bacterial nitroreductase (NTR) and are currently working on the targeting devices. To limit diffusion, the released LSD1 inhibitors will be so-called softdrugs which contain a breaking point for metabolic inactivation. We have developed LSD1 softdrugs already that are cleaved by cellular esterases and are currently establishing combined pro-softdrugs. Hence, we will induce an epigenetic event in a defined restricted space.
Publications resulting from the project
Nitroreductase-Mediated Release of Inhibitors of Lysine-Specific Demethylase 1 (LSD1) from Prodrugs in Transfected Acute Myeloid Leukaemia Cells.
Herrlinger EM, Hau M, Redhaber DM, Greve G, Willmann D, Steimle S, Müller M, Lübbert M, Miething CC, Schüle R, Jung M.
Chembiochem. 2020; doi: 10.1002/cbic.202000138.
KMT9 monomethylates histone H4 lysine 12 and controls proliferation of prostate cancer cells.
Metzger E, Wang S, Urban S, Willmann D, Schmidt A, Offermann A, Allen A, Sum M, Obier N, Cottard F, Ulferts S, Preca BT, Hermann B, Maurer J, Greschik H, Hornung V, Einsle O, Perner S, Imhof A, Jung M, Schüle R.
Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2019; doi: 10.1038/s41594-019-0219-9